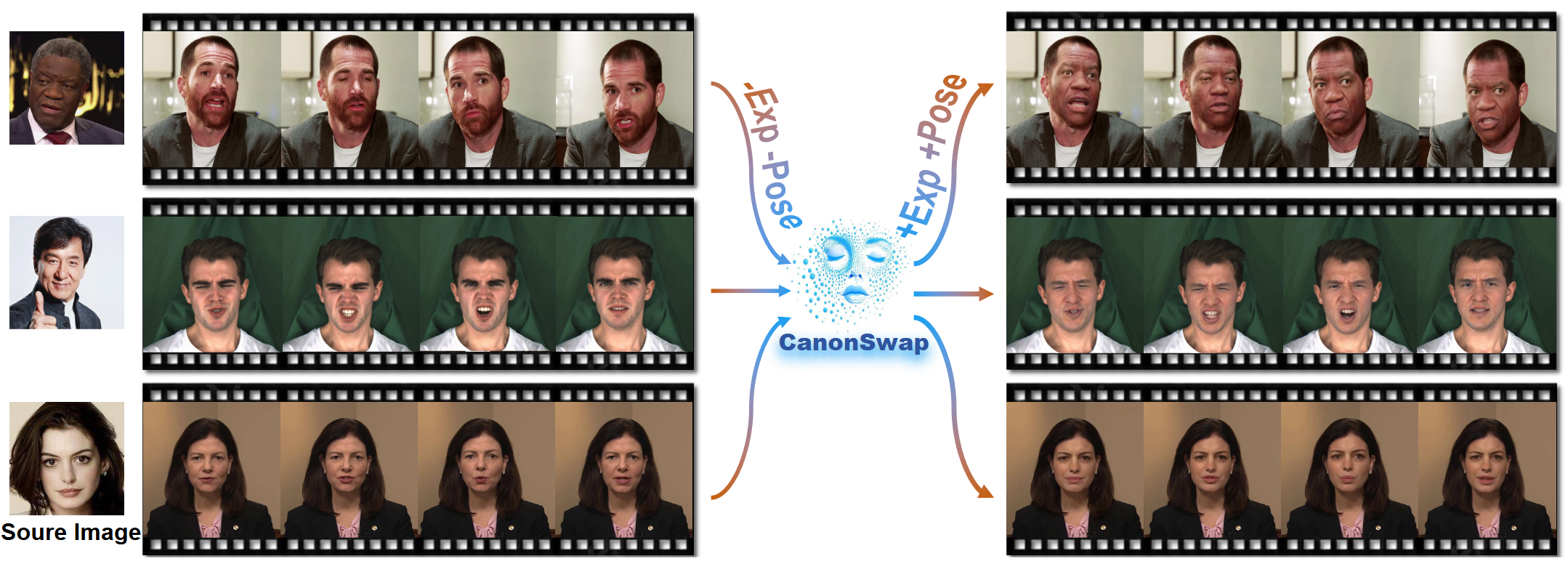
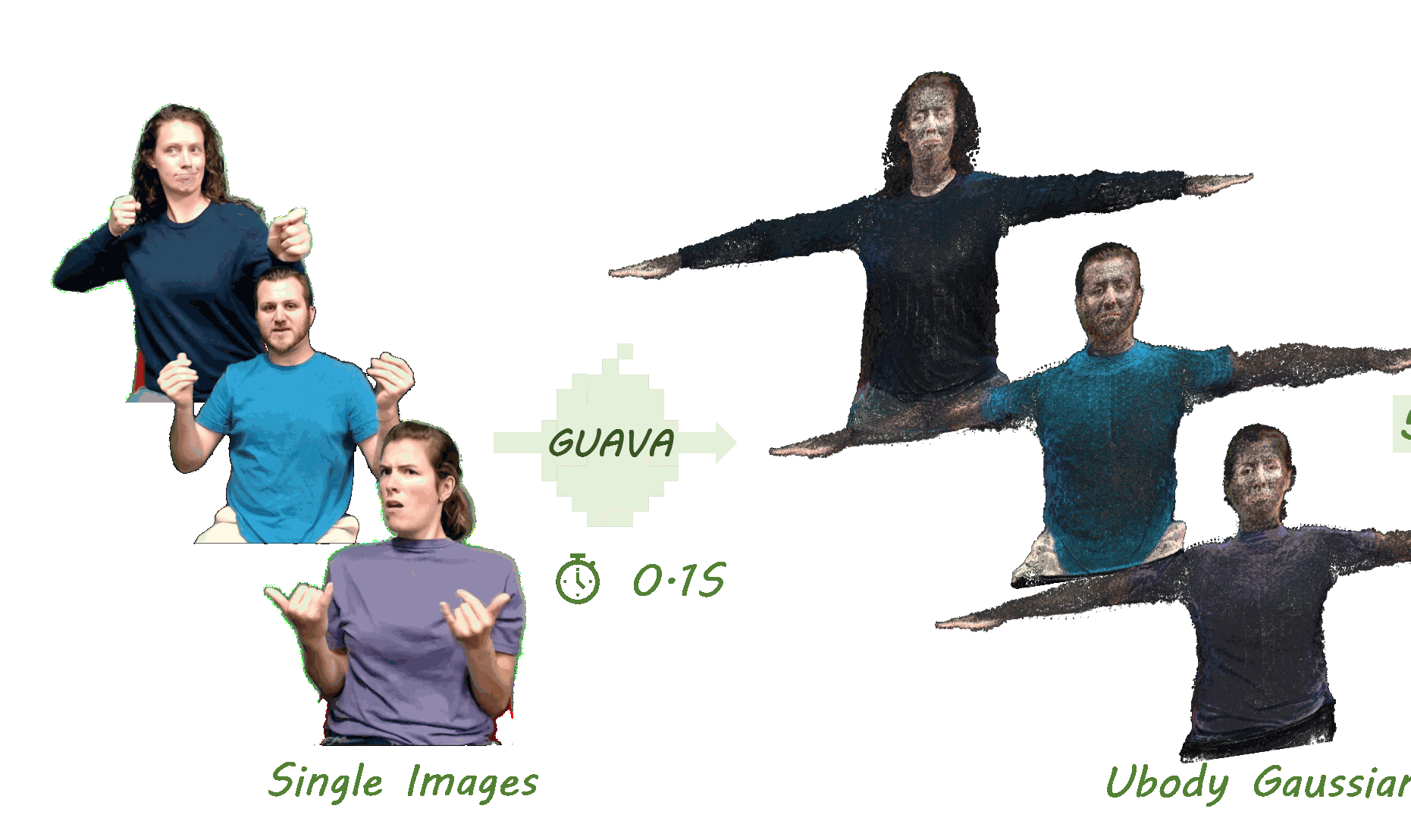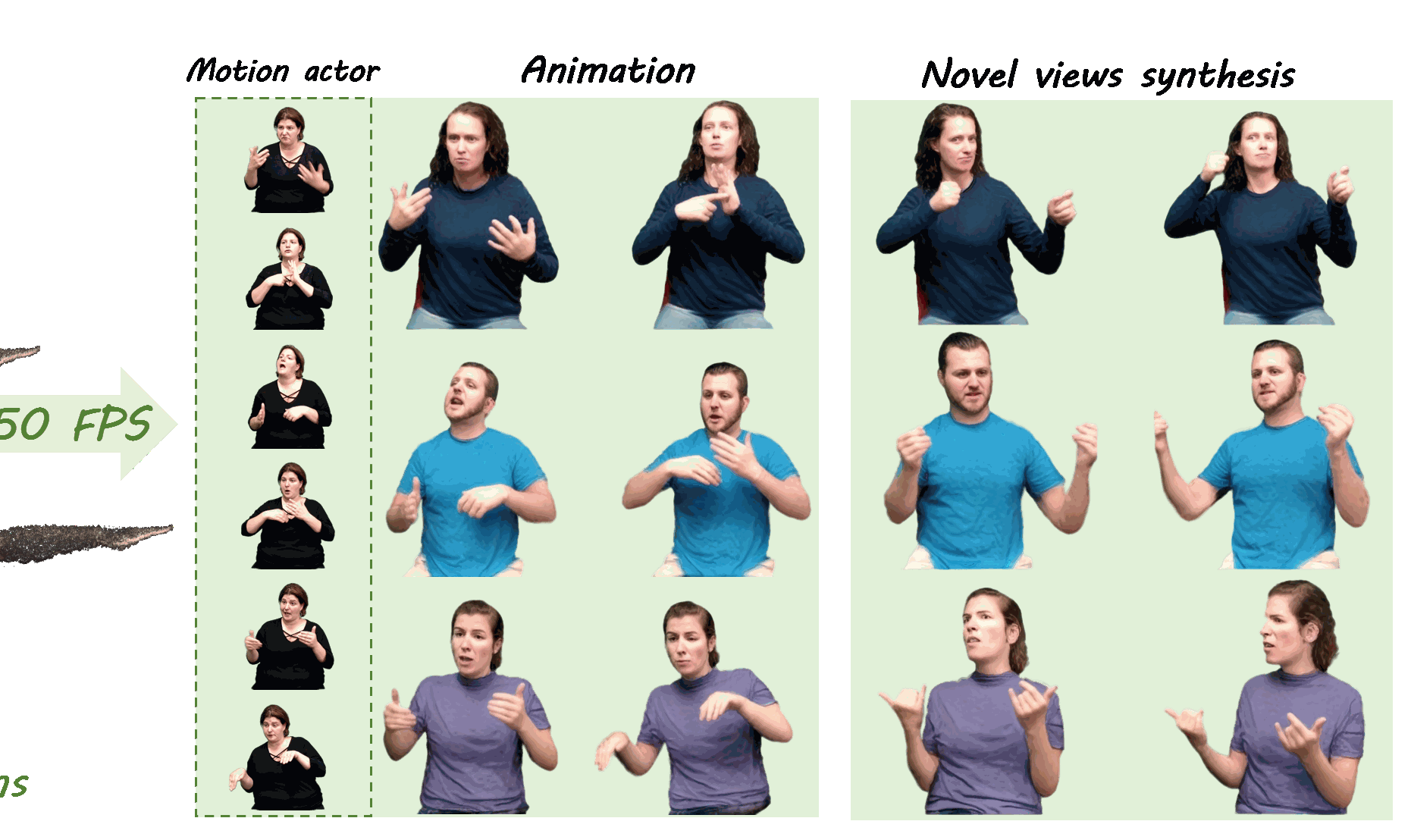
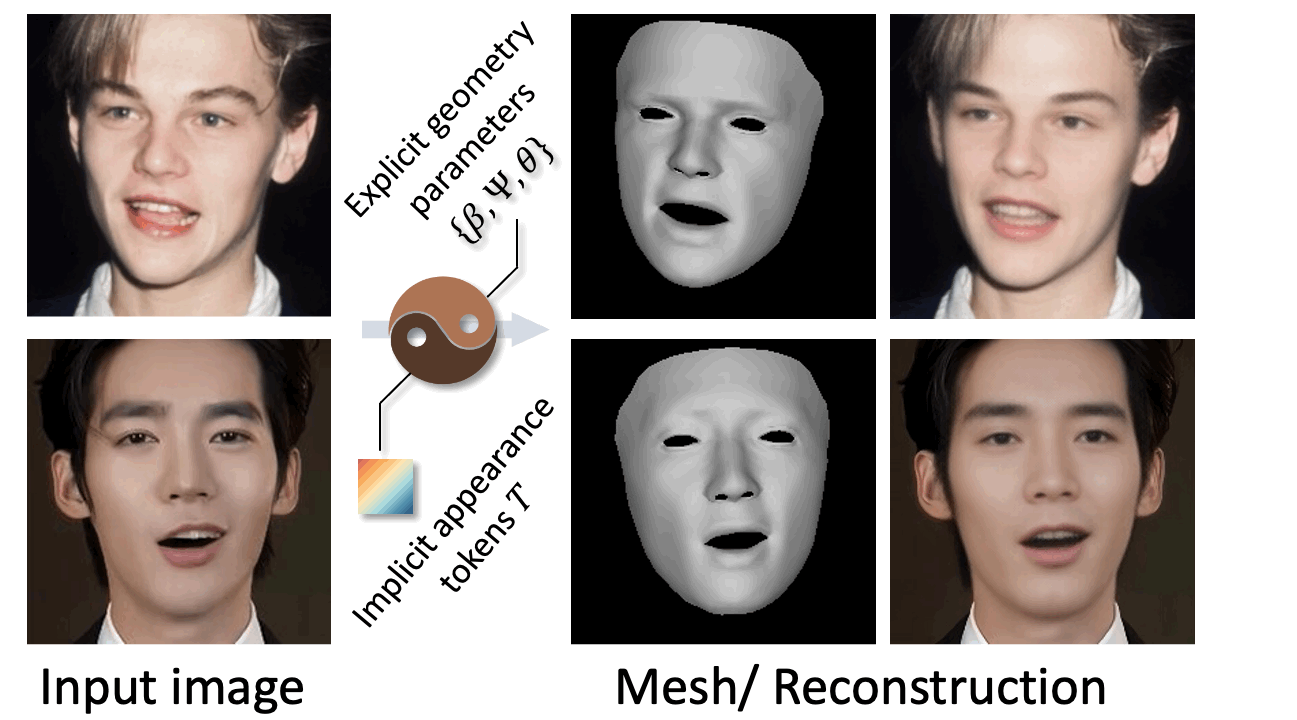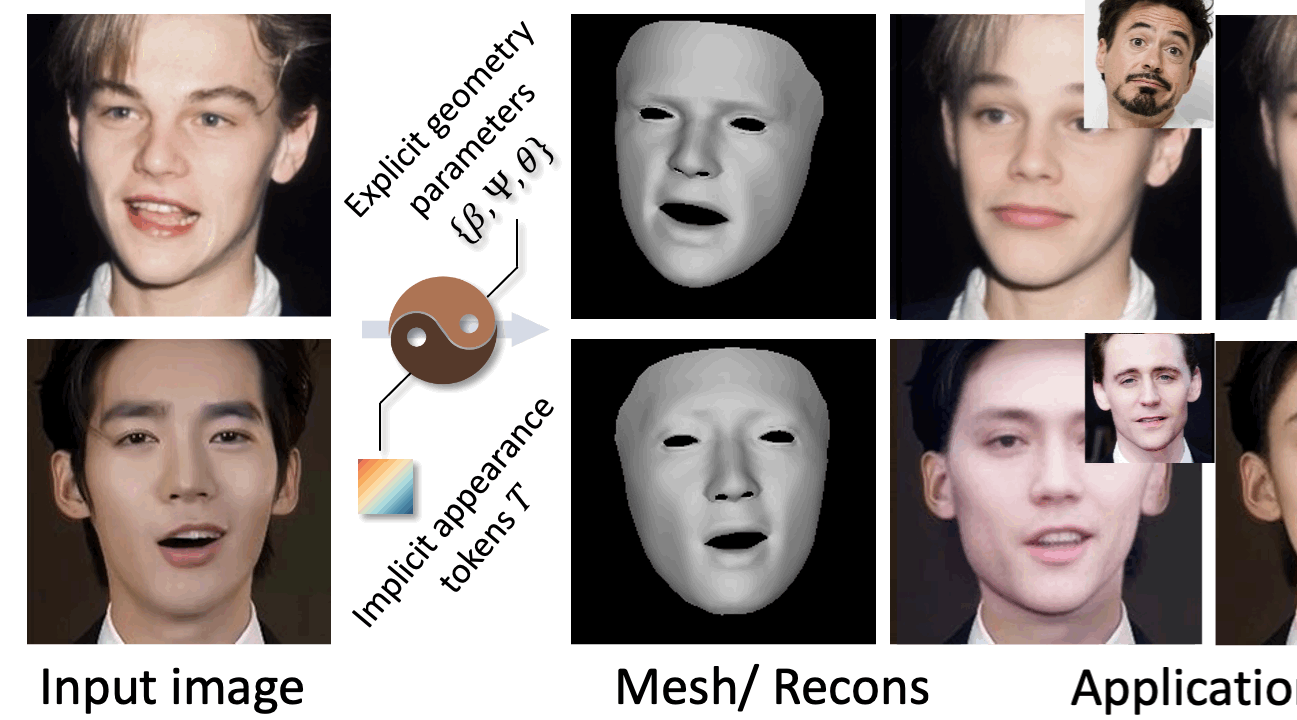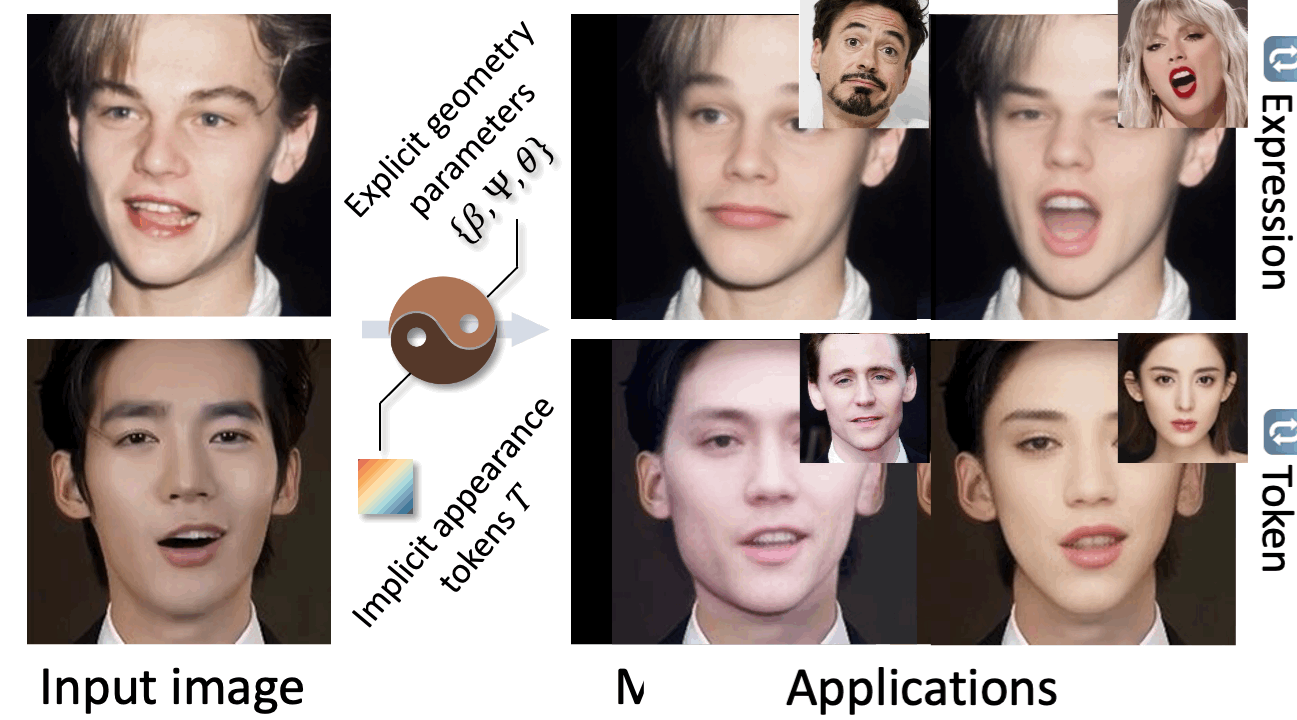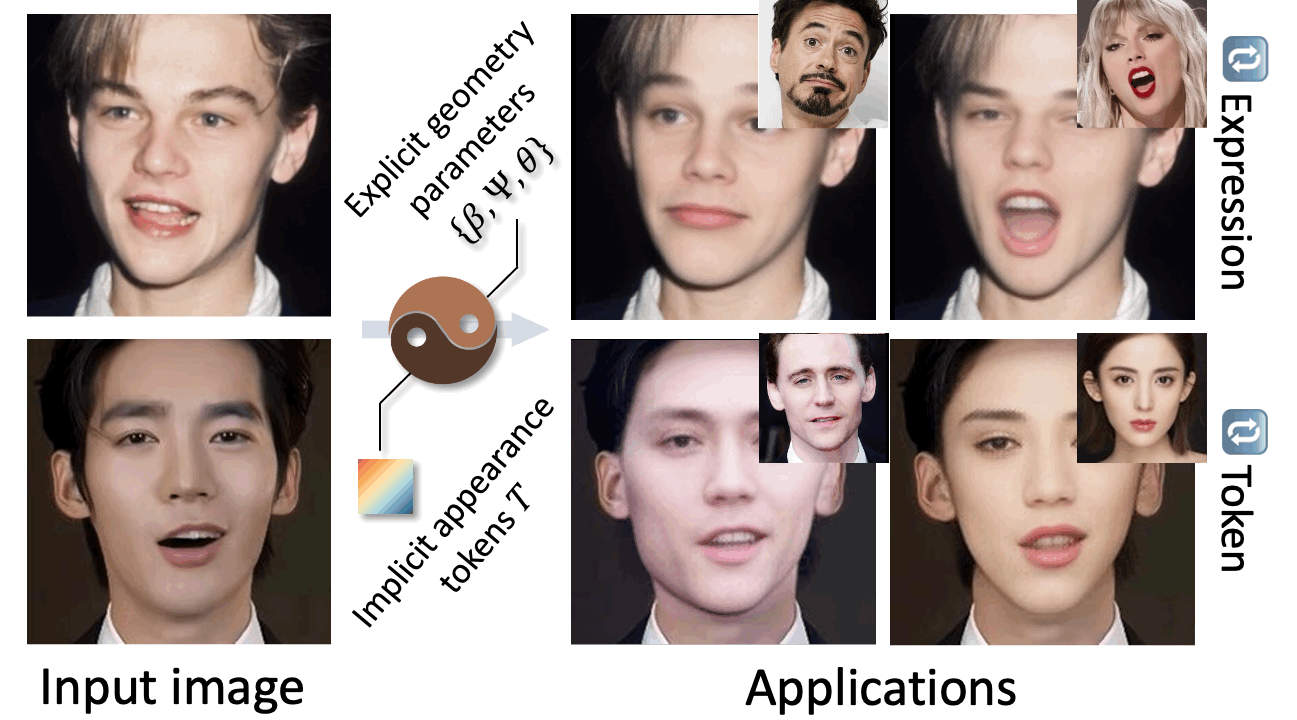
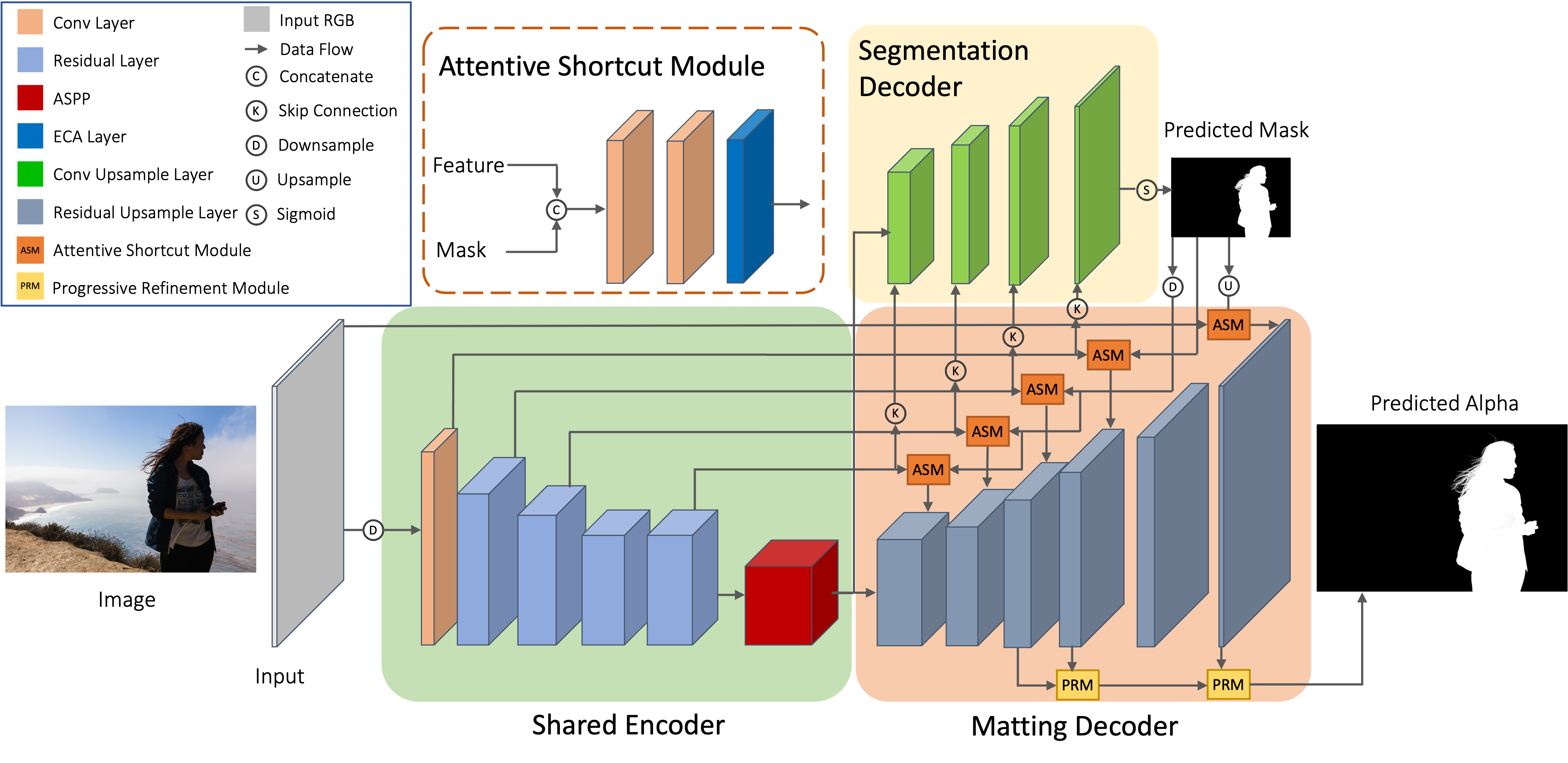
Previously, I got my bachelor's and master's degree from the South China University of Technology, advised by Prof. Yuhui Quan and Prof. Yong Xu
My research interests focus on visual content generation and editing (AIGC-related topics) and low-level image processing and segmentation.